Are all orthodontists Board Certified?
No. While all orthodontists must be licensed, only about one in three pursue Board Certification through the American Board of Orthodontics (ABO). Achieving this certification requires more than the standard two to three years of advanced education for orthodontic specialization and involves detailed case reports demonstrating expertise in treating various patient issues. Board certification is voluntary, and not all orthodontists opt for this path. To attain ABO certification, orthodontists undergo a comprehensive interview by a respected panel of examiners, showcasing their orthodontic knowledge, clinical skills, and judgment.
Key points about Board Certification:
- Extended Education: Beyond the standard two to three years of orthodontic specialization.
- Demonstrated Expertise: Through detailed case reports covering a range of patient treatments.
- Voluntary Process: Not all orthodontists choose to pursue board certification.
Comprehensive Interview: Assessed by a panel of respected examiners.
How many certifying boards are recognized by the American Dental Association in the specialty of orthodontics?
There is only one: the American Board of Orthodontics (ABO). Established in 1929, the ABO is the oldest specialty board in dentistry and the sole certifying board recognized by the American Dental Association. The primary goal of the ABO is to enhance the quality of orthodontic care by promoting excellence through certification, education, and professional collaboration.
Why would an orthodontist choose to complete this voluntary certification process?
Completing the certification process underscores an orthodontist’s commitment to excellence, benefiting both the profession and the public. It signifies that a licensed specialist possesses the necessary knowledge and skills to deliver top-tier patient care and demonstrates dedication to staying updated with the latest advancements in orthodontics. Many orthodontists view this certification as a testament to their specialty dedication and a significant personal achievement.
Reasons for pursuing Board Certification:
- Commitment to Excellence: Demonstrates the highest level of dedication to the field.
- Patient Care Standards: Ensures the orthodontist meets the highest standards in patient treatment.
- Continued Education: Shows a commitment to staying current with the latest orthodontic advancements.
- Professional Recognition: Seen as a significant personal and professional milestone.
What steps are required to complete the ABO certification process?
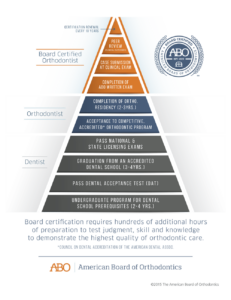
- Written Examination:
A comprehensive exam with 240 questions covering all necessary areas of orthodontic knowledge. - Clinical Examination:
Upon passing the written exam, orthodontists present detailed case reports from their practice or residency, demonstrating a history of excellence in patient care.
These cases are evaluated by a panel of examiners and discussed during an oral examination covering various academic and clinical topics. - Certification Renewal:
Certification is granted for a time-limited period, requiring renewal every 10 years. Orthodontists must demonstrate continued excellence in patient care to maintain their certification status.
For more information about the American Board of Orthodontics and Board Certification, click here.

